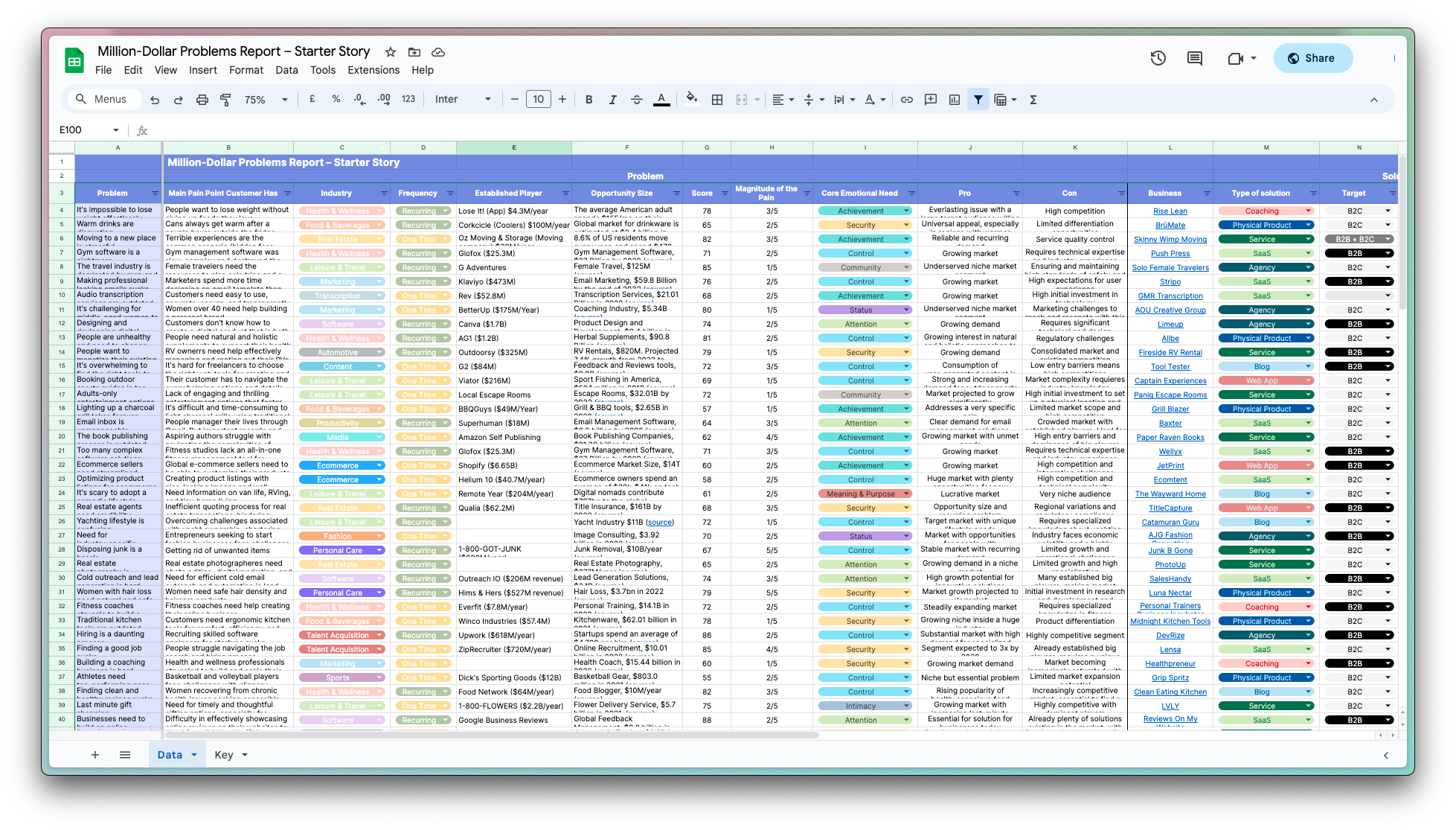
How Databricks Grew to a $62B Valuation in Just 11 Years
Who is Ali Ghodsi?
Databricks was co-founded by Ali Ghodsi, an engineer and entrepreneur from Sweden, who completed his Ph.D. in computer science at the University of California, Berkeley, and initially worked as a visiting scholar at its affiliated AMPLab.
What problem does Databricks solve?
Databricks helps businesses easily manage and process huge amounts of data, making data analysis faster and enabling smarter decisions with AI.
How did Ali come up with the idea for Databricks?
The idea for Databricks emerged when a team of seven researchers, while working at UC Berkeley's AMPLab, created Apache Spark. Apache Spark was developed to efficiently process large-scale data, and it quickly gained traction due to its unique ability to analyze messy data sets faster than existing solutions. The researchers saw a significant unmet need for a system that could help businesses leverage their vast data using advanced analytics and AI.
Before deciding to establish Databricks, the founding team sought validation of their idea by witnessing Apache Spark's rapid adoption and success in breaking world records, like sorting 100 terabytes of data significantly faster than previous tools. This success highlighted the technology's potential, encouraging the team to form a company that could commercialize the technology to solve real-world business challenges.
Despite initial doubts about fully committing to a technical executive role, Ali Ghodsi and his team refined their plans based on industry feedback, ensuring Databricks could address enterprise needs by enhancing software security and usability. A significant lesson from this process was balancing cutting-edge technology with strategic business practices, ensuring robust data management solutions appealing to large organizations seeking data-driven insights.
How did Ali Ghodsi build the initial version of Databricks?
Databricks was built on the foundation of Apache Spark, which was developed by its founders at the University of California, Berkeley. The initial prototype of Spark was created as a piece of code in a data-analytics lab that allowed for faster analysis of complex and messy data sets. This aspect of speed and efficiency became a unique selling point for Databricks, as they set a world record for processing 100 terabytes of data in 223 minutes, surpassing previous benchmarks. Building the first version was a technical endeavor, involving significant coding, testing, and iterations by a team of technical experts from Berkeley. Challenges included the need to shift from a free product model to a paid one, which required strategic adjustments and development of features that justified the pricing to attract enterprise customers, such as their notable early customers Capital One and JPMorgan. Integrations with major platforms like Microsoft also posed challenges, but eventually resulted in lucrative business deals, exemplified by a $100 million sales deal with Microsoft in 2017.
What were the initial startup costs for Databricks?
- Initial Funding: The founders asked for $200,000 from Ben Horowitz, who instead provided $11 million through his venture-capital firm Andreessen Horowitz.
What was the growth strategy for Databricks and how did they scale?
Partnership with Microsoft
Databricks formed a strategic partnership with Microsoft in 2017, which became a significant growth channel for the company. This collaboration integrated Databricks' platform into Microsoft's Azure cloud services, making it easier for users to adopt Databricks through a trusted and widely-used platform. The partnership contributed notably to their revenue, with $100 million in sales generated through this channel.
Why it worked: By aligning with Microsoft, Databricks gained access to a larger pool of potential customers already using Azure. The partnership added credibility to Databricks' offerings and provided an effective avenue for scaling their business through an established distribution network.
Charging for Software Features
Initially, Databricks faced challenges in monetizing their offerings as their software was available for free. After Ali Ghodsi became CEO in 2016, the company began charging for access to enhanced features. This shift motivated enterprise clients, including major financial institutions like JPMorgan and Capital One, to become paying customers.
Why it worked: Transitioning to a paid model encouraged larger organizations to invest in Databricks' solutions for their competitive advantage. This strategic move successfully diversified their revenue stream and increased the perceived value of their software offerings.
AI and Automation Innovations
To boost productivity and maintain growth, Databricks implemented AI-powered tools such as the R2-D2 bot. This innovation helped automate processes and enhance efficiency within their operations. The company also strategically invested in acquiring MosaicML to expand their AI capabilities and refine their machine-learning models.
Why it worked: Leveraging AI allowed Databricks to streamline business processes and improve their products, reinforcing their position in the AI and data analytics space. These technological advancements made their platform even more attractive and effective for businesses, further driving sales and customer retention.
What's the pricing strategy for Databricks?
Databricks employs a usage-based pricing model, where costs scale with data processing and storage needs, and offers a free tier for limited usage.
What were the biggest lessons learned from building Databricks?
- Strategic Pricing Changes: Databricks initially offered its software for free, which posed challenges in monetization. They overcame this by introducing a pricing model that restricted access to paying customers only, targeting large enterprises like Capital One and JPMorgan.
- Embrace Technical Sales: For a complex, technical product, having a sales team with strong technical expertise proved essential. This approach built trust with technical buyers and enhanced sales effectiveness, a strategy critical for Databricks' growth.
- Investor and Team Alignment: When faced with growth challenges, CEO Ali Ghodsi responded to investor suggestions by slowing down hiring and focusing on internal productivity, using AI-driven tools to maintain company efficiency.
- Transparency and Shared Vision: Sharing board presentations with employees created alignment and motivation across the company, ensuring everyone worked towards common goals.
- Resilience and Innovation: Instead of layoffs during tough times, Databricks focused on innovation to drive profitability, such as developing AI bots like R2-D2 to enhance productivity and sales efficiency.
Discover Similar Business Ideas Like Databricks
|
|
Idea
|
Revenue
|
|---|---|---|
|
PDFShift
|
HTML-to-PDF conversion API service.
|
$8.5K
monthly
|
|
SiteGPT
|
AI chatbot trained on your website content.
|
$15K
monthly
|
|
Hallow
|
"Catholic prayer and meditation app fostering faith growth."
|
$278K
monthly
|
|
tiiny.host
|
Static website hosting made simple for everyone.
|
$15K
monthly
|
|
Studio Wombat
|
WooCommerce plugin developer for enhanced e-commerce features.
|
$15K
monthly
|
|
Treendly
|
Trend-spotting platform for untapped market insights.
|
$1K
monthly
|
|
ScreenshotOne
|
API for capturing website screenshots easily.
|
$2.2K
monthly
|
More about Databricks:
Who is the owner of Databricks?
Ali Ghodsi is the founder of Databricks.
When did Ali Ghodsi start Databricks?
2013
What is Ali Ghodsi's net worth?
Ali Ghodsi's business makes an average of $200M/month.
How much money has Ali Ghodsi made from Databricks?
Ali Ghodsi started the business in 2013, and currently makes an average of $2.4B/year.

Download the report and join our email newsletter packed with business ideas and money-making opportunities, backed by real-life case studies.

Download the report and join our email newsletter packed with business ideas and money-making opportunities, backed by real-life case studies.

Download the report and join our email newsletter packed with business ideas and money-making opportunities, backed by real-life case studies.

Download the report and join our email newsletter packed with business ideas and money-making opportunities, backed by real-life case studies.

Download the report and join our email newsletter packed with business ideas and money-making opportunities, backed by real-life case studies.

Download the report and join our email newsletter packed with business ideas and money-making opportunities, backed by real-life case studies.

Download the report and join our email newsletter packed with business ideas and money-making opportunities, backed by real-life case studies.

Download the report and join our email newsletter packed with business ideas and money-making opportunities, backed by real-life case studies.